Inworld Beyond 2024
Beyond first-generation applications of AI in gaming
"Seeing [Inworld’s] tech in action has me excited for the future of gaming in a way that I can’t say I’ve felt in quite a while. Done right, this is the kind of tech that, much in the same way that the jump from 2D to 3D… could lead to entirely new kinds of games and experiences."
- IGN
In the 90s, early 3D games like Wolfenstein 3D and Doom marked a key turning point in games. Despite their relatively rudimentary graphics, they heralded the potential for games with more immersive worlds and visceral mechanics. That early promise has since been realized in modern titles like Tears of the Kingdom or Ghosts of Tsushima thanks to game devs that creatively leveraged technological advancements to push the bounds of what’s possible in games.
The advent of large language models has ushered in a similar new era of possibilities. The earliest applications of AI within gaming have been focused on intelligent NPCs. But as we look ahead, just like with 3D graphics, the true potential of AI in gaming will be unlocked by game developers who harness these models to develop new gameplay mechanics that were previously inconceivable.
We recently shared a glimpse of what that future might look like during Inworld Beyond, our webinar on the future of AI in gaming.
Overview of Inworld Beyond
- Beyond LLMs
- Beyond conversation
- Beyond crunch
- The economics of AI-powered gameplay
- The future of AI in games
Beyond LLMs: Inworld AI Components as building blocks for AI gameplay
AI NPCs (non-player characters), enemies, and opponents in video games are typically designed to interact with players and the game world in predefined ways, often according to a script. In contrast, AI Agents are more autonomous, capable of making decisions and taking actions based on motivations, objectives, and the game context, allowing for more dynamic and adaptable behavior.
Inworld's AI agents go beyond a simple prompt and draw from a pipeline of specialized machine learning components. This modular system of Inworld AI Components – that include both models and systems – enables our AI to generate complex, context-aware behaviors that go beyond LLMs to provide gameplay mechanics that respond to the evolving state of the game world and player inputs.
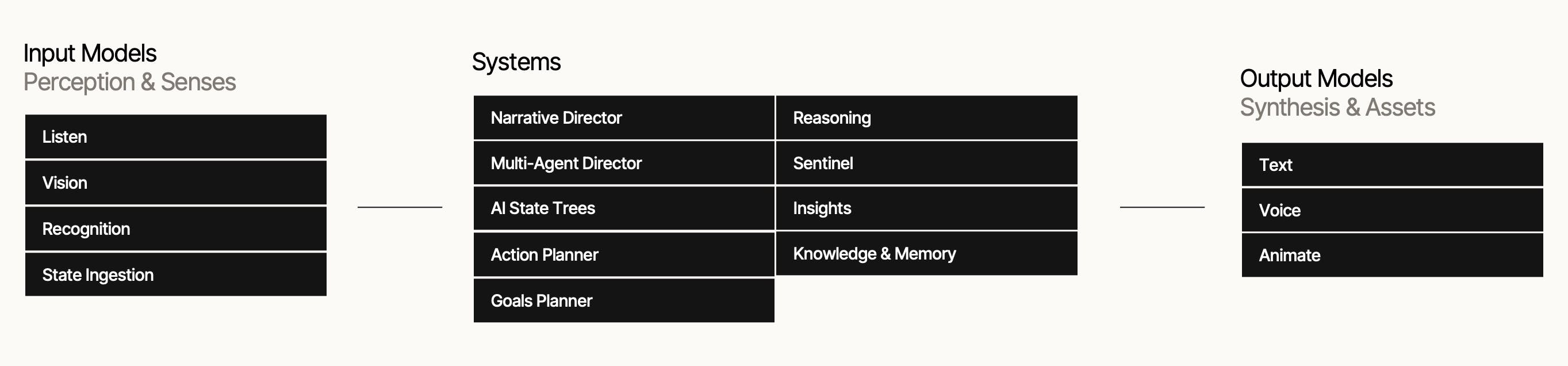
Beyond conversation: Enhancing games with agentic AI
Inworld AI Components allow AI agents to take lifelike actions using a blend of decision-making algorithms, perception systems, and adaptive learning. From the simple patrol routes of a guard to the complex group tactics of enemy squads, Inworld ensures that characters behave in ways that are both believable and challenging, creating a richer, more engaging experience for players.
Let’s take a look at a few demos that illustrate how AI agents can be leveraged in video games.
Crafting engaging AI companions & co-op play
Companions, followers, sidekicks, guides, party members – whatever you call them – they’re the NPCs that have the most impact on a player's experience of your game. In the following demos, we’ve created AI companions that leverage AI Components to provide real-time tactical support, co-op play, and respond to the player and environment with increased environmental awareness.
Bringing game worlds to life rapidly
Fans of RPGs crave worlds that feel real, with a cast of believable characters that draw you deeper into the fantasy. These vast worlds can be intensive to populate, but with Mass Character Generator, you can create NPCs at scale during design-time or in-game to allow players to customize the game world. Player commands are processed with speech-to-text, triggering mass character metadata generation that users can connect to their own licensed or owned asset libraries to connect character brains with their existing game assets. This system also allows characters to be governed by existing game knowledge or safety guidelines, all in real-time.
Here is a further breakdown of the AI Components being used:

Creating dynamic dialogue trees
Dialogue trees can feel restrictive for players, as they often limit choices to predefined options, preventing more natural, fluid interactions. Inworld Text, our LLM service, uses AI to automatically generate adaptive dialogue options that react to player inputs in real-time. It can also craft detailed lore codex entries and generate player summaries.
Each of these demos were made possible by Inworld AI Components, which provide the flexibility to power AI agents for various gameplay scenarios.
AI NPCs are just one type of AI agent that can be implemented in games. Beyond NPCs, agents in video games can serve as tools for procedural generation, dynamically creating vast landscapes, quests, and narratives. They can also function as adaptive difficulty systems, adjusting the game's challenge level based on the player's skill level and preferences. Agents can also govern the behavior of objects and physics, adding fluid dynamics and movement to a living game world.
Action Planning in Video Games
Game devs have typically powered character behavior using techniques such as Finite State Machines (FSMs), behavior trees, or Goal-Oriented Action Planning. While these techniques are effective for managing simple and well-defined behaviors, they can become brittle and complex at scale, leading to gameplay that feels predictable and repetitive.
Inworld's Multimodal Action Planning and AI State Tree features offer more dynamic alternatives to traditional action planning AI. These systems allow AI agents to generate actions in real-time, responding adaptively to the game environment and player behavior.
Project Multimodal Action Planning
Inworld’s MAP (Multimodal Action Planning) project lets developers create AI agents with an awareness of in-game objects and actions, enabling them to autonomously reason through objectives and plan action sequences. MAP leverages game state information to allow NPCs and AI agents to execute actions based on motivations and objectives, eliminating the need for extensive scripting or explicit triggers. MAP will respond to three different stages of action planning:

- Surrounding awareness enabled by Inworld’s Perception systems, which allows agents to recognize entities, intents, and more
- Self-driven actions
- Planning steps
By simplifying the orchestration of complex behaviors, MAP enhances AI responsiveness, fosters more immersive interactions, and offers developers greater customization and creative freedom in designing dynamic game worlds.
Project AI State Tree
Traditionally, crafting a game's state machine involved painstakingly hard-coding every possible state and transition, a process that is not only time-consuming but also limited in flexibility. At Inworld, we’ve been developing AI State Trees to understand the impact AI can have on state management. We are currently experimenting with configuration of state trees from simple scripting that provides AI capabilities in detecting and adjusting a character’s behavior to the player. Additionally, we are experimenting on generating state trees at runtime to aid goal planning that is adaptive to players.
This adaptive approach transforms rigid finite state machines into dynamic, responsive systems capable of evolving in real-time. The result? More complex and nuanced in-game behaviors and dialogue with less coding, enabling you to push the boundaries of what’s possible in game design.
Beyond crunch: AI-assisted game design & development
AI can open doors to new types of experiences, narratives, and gameplay when AI agents and NPCs are added to games – but it can also be used as a tool to accelerate game development and design.
As the costs of developing games skyrocket and the thirst for content grows, developers can leverage AI to streamline production and get games to market more quickly. We’ve developed a suite of game design tools that assist with prototyping and drafting narrative and content.
Developer-facing AI tools
- Narrative Graph, co-developed with Xbox, helps visualize and manage interactive narratives by auto-generating branching storylines from uploaded content.
- Scriptwriter is an AI writing assistant for drafting game dialogue, offering context-aware suggestions based on the game's world and characters.
- Barks Generator produces and records NPC barks at scale, efficiently populating game worlds with diverse, authentic NPC interactions.
- Voice Studio lets developers record voiceovers with synthetic AI voices, providing a cost-effective solution for adding expressive voice acting to games.
- Mass Character Generator automates the creation of AI NPCs by generating thousands of unique characters directly in your game engine, using an asset library linked to a placeholder NPC template.
The economics of AI-powered gameplay
One frequently cited concern around leveraging generative AI in games is the expense of LLM calls, especially when it comes to real-time gaming. But since ChatGPT launched in late 2022, the cost of using large language models has gone down considerably – and is expected to continue to do so. At Inworld, we’ve focused on optimizing our costs so we can pass the savings onto our users.
These cost savings come from:
- Optimizations in model architecture. We optimized models to increase throughput with minimal quality degradation via quantization, batching, KV-cache optimizations, and more.
- Model size vs. quality improvements. For many use cases the optimization and adaptation of a smaller model can lead to 2x to 10x cost decreases, with minimal or no quality degradation. While this is not always possible for every use case, it is for many use cases.
- Better inference server algorithms. We’ve been able to improve inference server algorithms with the introduction of SoTA methods, deploying optimized kernels, KV-cache optimizations, better request scheduling/routing, and more.
- Moving some models or inference on-device: We’re committed to working to move models on device, when possible both currently and in the future. We’re working on creating smaller models with better performance and demonstrated a hybrid on-device and cloud deployment with NVIDIA at Computex.
- Many other improvements. We’ve also achieved latency and cost savings by combining models so they work optimally together, and more.
Additional optimizations and efficiencies are expected in the next couple of years with the possibility of serving even more types of models and use cases on-device. What’s more, gamers are eager for AI gameplay – and studies show they are willing to pay for it.
Case Study: Optimizing costs on a game generating 1.2B AI tokens
Playroom recently launched the AI-powered party game Death by AI, reaching a massive audience of nearly 20 million users within the first two months, resulting in 1.2B AI tokens being generated and the need to support thousands of daily game sessions. Learn why they switched to Inworld when they needed gaming-optimized latency and pricing.
Future of AI in games
One of the gaming industry’s biggest strengths is its ability to imagine what new technologies can make possible – and then to make those things possible. As we look ahead, we believe the true potential of AI in gaming will be realized not in its first-generation applications, but in the places where artists, developers, and narrative designers are leveraging AI in innovative ways to go beyond what’s currently possible in games.
At Inworld, we’re excited to build the next generation of games with you.