Check out what's new:
AI agents in video games will transform matchmaking
Explore the potential of generative AI agents to enhance multiplayer experiences by providing more dynamic and adaptable gameplay.

There’s a reason why gamers wait so long in lobbies to be matched with human players. They often feel that today’s AI players lack the adaptability and creativity of human players – which leads to less dynamic and engaging matches. Common complaints about current AI players include their predictable behavior, lack of strategic decision-making, and inability to provide the same level of challenge as human opponents.
But AI players powered by generative AI agents are expected to transform multiplayer experiences – and, in doing so, greatly reduce those lobby wait times and improve matches by ensuring a better skill level balance. They can potentially also be deployed to take over when one of your team members has to leave mid-game or can’t join that evening’s gaming session. AI agents could even mimic the gameplay of that particular player.
Given the excitement around AI agents in video games, it’s not surprising that our recently released Future of Game Development with AI NPCs report found that game devs think AI players in multi-player games are the second most likely NPCs to be powered by generative AI in the next 10 years.
As game developers seek scalable solutions for matchmaking, player retention, and engagement, AI agents are expected to bridge this gap. From enhanced player engagement and personalized gameplay to reduced toxicity and stress, the integration of AI agents into multiplayer games promises to solve a number of key pain points.
Challenges with matchmaking today
Matchmaking in online multiplayer games is a pain point for all games, no matter the size of their player base. Research shows that players that routinely have bad experiences or are outskilled in matches are much more likely to churn. A 2024 study analyzing over 1 million matches in competitive games found that the greater the difference in the skill gap between players, the higher the churn rate.
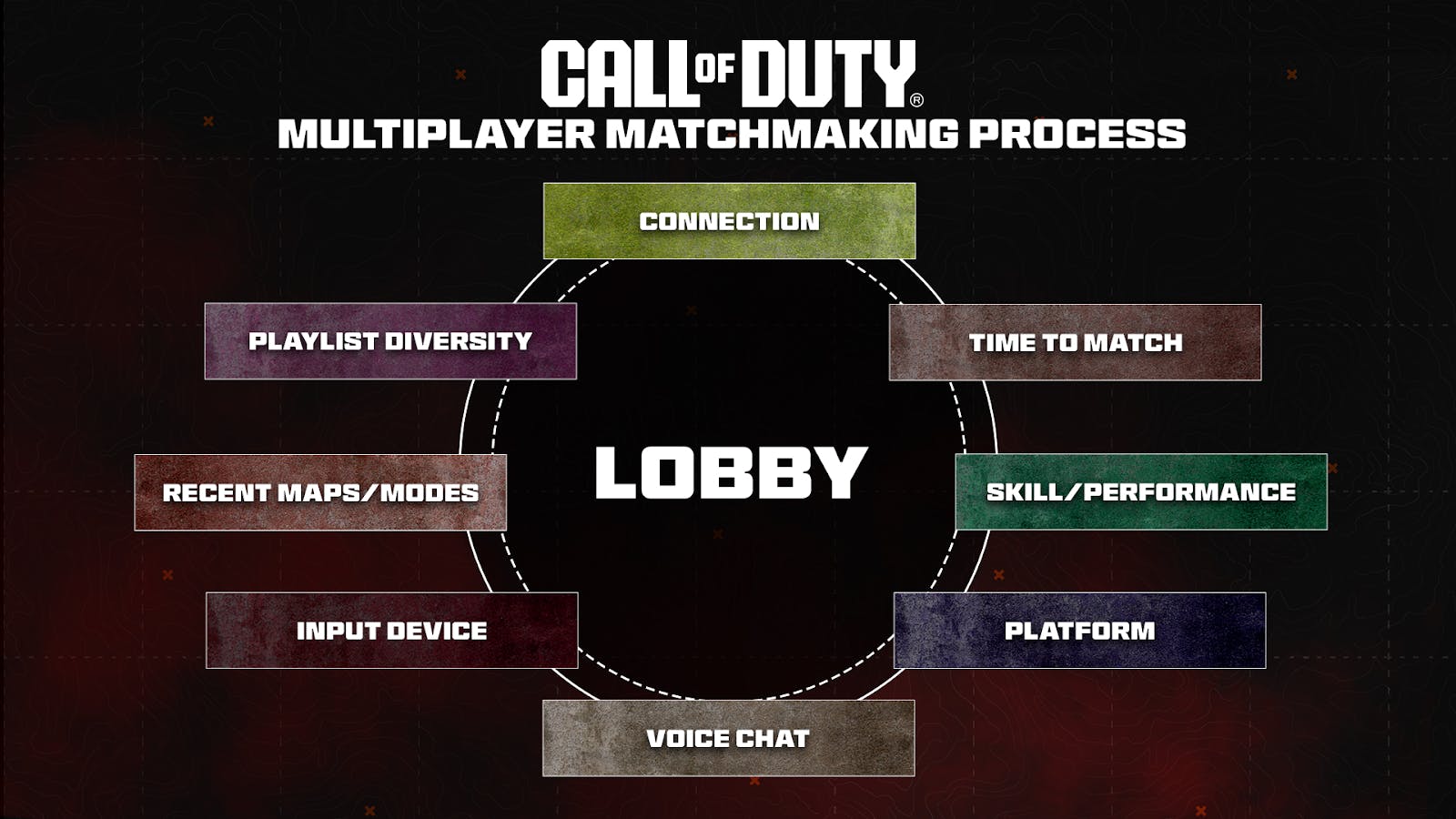
But effective matchmaking is complex since there are a wide range of factors that contribute to creating a balanced match. Call of Duty, for example, recently wrote a blog post about their matchmaking process showing that it weighs things like player ping, time to match, skills/performance, platform, whether voice chat is enabled or disabled, input device, recent maps/modes, and playlist diversity to create the optimal match.
Each factor reduces the pool of players that can be matched together at any given time. This creates additional complexity and adds additional time to matchmaking in games with longer average match length or a larger number of players per match. That makes creating good matches especially challenging during off-peak times or in regions with lower player counts.
However, waiting too long in the lobby for the optimal match also increases churn. Games, therefore, have to decide between two churn-inducing options - longer lobby wait times or imbalanced matches.
Generative AI agents that players enjoy playing against present a solution to both of these problems. This would be a scalable solution for game developers that ensures that games are more accessible and enjoyable for all players regardless of skill level and location – something that’s likely to boost player retention and extend playtime.
Current state of AI agents in video games
Thanks to recent advancements in large language models (LLMs), AI agents have the capacity for much more sophisticated behavior than was possible before. A prime example of these advancements is Stanford University's ‘Stanford Village’ project, where researchers created a virtual environment populated by AI agents with the ability to plan and carry out complex actions autonomously. These agents could engage in complex actions and social behaviors, such as deciding to host a party and planning it or forming relationships with NPCs or players.
Similarly, Google's DeepMind AI research has made significant strides in developing more autonomous and adaptable game agents. Projects like DeepMind's AlphaStar have demonstrated that AI can learn to play complex games like StarCraft II at a professional level. These agents use deep reinforcement learning to understand the game's mechanics, develop strategies, and adapt to opponents' tactics in real-time. Meanwhile, Google’s Scalable Instructable Multi-Agent (SIMA) project taught AI agents how to complete 600 video game skills and complete complex multi-step actions.
Inworld is also working at creating autonomous AI agents for video games – but with a focus on creating agentic behavior in AI agents that developers are able to direct and control, rather than freeform action. Towards that end, we’ve released features like our Goals and Actions feature that allows AI agents to be given motivations that they can act on when they determine that they’ve been triggered by the player or game environment. We’ve also created a soon-to-be-launched Configurable Reasoning module that adds a context-rich reasoning step to enable all types of agentic motivated behaviors and actions. Finally, we’re hard at work on more features that will allow developers to add the type of agentic multi-step actions and behaviors to AI agents that would better power AI player use cases for matchmaking in multiplayer games.
The sophistication of the experiments above mark a significant milestone in the evolution of AI in gaming – and suggest that much more advanced AI players are on the horizon.
For a more in-depth look at the research into AI agents in video games, see our article on it.
The future of AI players
As generative AI continues to evolve, expect AI agents to be capable of more complex autonomous actions because of increases in reasoning and action orchestration capabilities. This will make them perfect as AI players since they’ll be able to react directly to in-game actions and showcase emergent gameplay.
These future AI players will possess advanced decision making, autonomous actions, improved contextual awareness, improved memory, and improved conversational skills. This improve their game play and make them more strategic, more adaptable to diverse play styles, and more customizable to the players in that match rather than rigidly following an algorithm.
These autonomous AI players would be challenging opponents and helpful teammates who could dynamically adjust their skill level to the level of the players – and even talk with other players during gameplay via voice or chat like human players do.
By genres: What the future of AI players will look like
While AI players offer the potential for improving matchmaking in multiplayer games by ensuring balanced matches and reducing lobby wait times, that’s not all they’ll be able to do.
AI agents also have the potential to improve AI players by providing them with a number of new capabilities. Here are some examples of how various genres could take advantage of this.
Shooter games
AI players in Shooter games powered by AI agents could feature advanced enemy behavior including adaptive tactics, dynamic decision-making, and realistic teamwork. For example, enemies could coordinate flanking maneuvers, use cover intelligently, communicate with each other or players on their team via voice chat to outsmart opponents, and learn and adapt to player behavior.
Racing games
AI agents could simulate entire racing teams with distinct personalities, driving styles, and strategies. In a Racing game, AI-controlled rival teams could compete against the player with realistic racing tactics, such as drafting, blocking, and strategic pit stops.
Sports games
AI agents could play on your team or be your opponents. They can provide commentary and chatter while adjusting tactics on the fly. AI agents could also simulate realistic player behaviors and interactions, enhancing the authenticity of Sports games by exhibiting dynamic emotional reactions, communicating with teammates, and adapting their play style based on game situations and opponent strategies.
RPGs
AI agents could create dynamic opponents or NPCs with complex personalities, motivations, and relationships to fill up online game worlds during off-peak times or in time zones with lower player numbers. For example, fantasy RPGs could use AI players to populate the game world with NPCs that have their own goals and agendas. This could allow them to form alliances, betray allies, and influence the game world in unpredictable ways.
Strategy games
AI players play pivotal roles in Strategy games, serving as opponents or allies in complex tactical scenarios. For example, strategy franchises like Civilization could employ AI agents to simulate diplomatic negotiations, trade interactions, and military strategies which would greatly enhance the depth and realism of the gameplay experience.
The impact of improved AI players on multiplayer games
Aside from improving matchmaking by making it faster and more balanced, there are a number of other benefits AI agents are likely to generate when deployed as AI players in multiplayer games. Many of these will contribute directly to improving metrics, revenue, and player satisfaction.
More accessible gaming
AI agents can help make multiplayer games more accessible to players of varying skill levels by filling up matches with AI players who can adapt their skill levels to that of the players.
More advanced AI teammates could also help less experienced players in cooperative matches to provide a supportive environment for skill development. For example, that could include things like having AI agents provide cover to players on their team who are still learning or act as a companion during missions while players are onboarding.
This would help games with new player retention and create a more diverse player base, something many online multiplayer games struggle with.
Increased player convenience and flexibility
AI agents can be used by players to take over gameplay for them when they have to step away from a match with friends – or when they can’t join a particular game. AI agents can even be taught how to imitate the player’s play style and role within the team in order to be effectively swapped in as a replacement.
This would provide gamers with more flexibility and convenience by allowing them to step away temporarily during matches or have their AI replacement join matches they can’t make.
More innovative gameplay
AI agents could create more innovative gameplay experiences by introducing new gameplay mechanics and dynamics. For example, they could showcase advanced tactics and strategies that inspire players to experiment and learn new approaches.
AI agents could also offer more personalized experiences by adapting to individual player preferences and playstyles. For example, AI-controlled opponents could adapt their tactics and strategies based on player skill level and performance, offering a more rewarding and immersive gaming experience.
Reduced toxicity and stress
AI agents can help reduce toxicity and stress in multiplayer games by providing a more positive environment and allowing teams to round out their party with AI players rather than strangers.
According to a 2023 report by Bryter, a whopping 65% of female gamers experience toxicity in gaming communities. This leads women gamers to avoid online multiplayer games. In fact, 39% have chosen to leave the match or lobby and 24% have chosen to leave the game completely when they’ve experienced toxicity. Around one third of women said they wanted to play more multiplayer games but are put off by the toxicity. Other groups also report experiencing toxicity in online gaming communities such as younger players or minority players.
AI agents in multiplayer games would allow greater control over who you play with since solo players could choose to play entirely with AI agents or only with people they know.
Potential for monetization
AI agents also offer potential monetization opportunities through in-game purchases, expansions, or subscription models. For example, in a free-to-play multiplayer game like Apex Legends, players could purchase AI-controlled squadmates as companions or hire mercenaries to assist them in battles. Similarly, players could pay for an AI agent that could take over for them temporarily when they’re unable to play.
This would provide additional revenue streams for the developer while enhancing the gameplay experience for new players and players and increasing retention by streamlining matchmaking and ensuring better balanced matches.
The future of AI players in multiplayer games
These are just a few examples of what the future of AI players in multiplayer games might look like. Expect game devs to come up with even more ways to integrate generative AI in multiplayer games in ways that streamline matchmaking and enhance the experience for gamers.
Currently, game devs can add advanced AI systems to games via AI NPCs powered by AI Engines like Inworld’s. That can introduce novel game mechanics like relationship progression triggers, dynamic Character Mutations, and voice commands.
Inworld’s core future development focus is on increasing AI agent autonomy in games by developing features focused on action orchestration and reasoning to ensure that AI player use cases will soon be a reality.